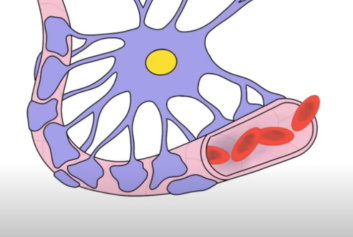
Blood-brain barrier
A protective barrier that separates the brain from the blood circulating across the body.
The blood-brain barrier is semipermeable, meaning it allows the passage of water as well as molecules like glucose and other amino acids that help promote neural function. Blood–brain barrier dysfunction contributes to pathology in a range of neurological conditions including multiple sclerosis, stroke, and epilepsy, and has also been implicated in neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease.
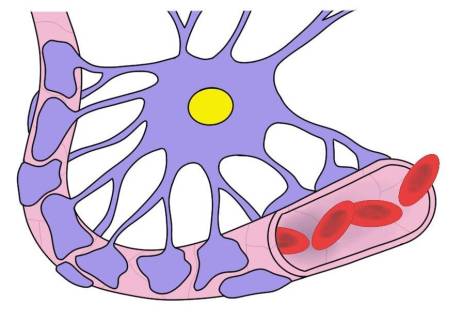
Image credit: https://www.neuroscientificallychallenged.com/blog/know-your-brain-blood-brain-barrier
Find out more about your blood-brain barrier
Learn how the blood-brain barrier protects your brain and what happens when it fails.